

Real-Time Analytics with Memory-Optimized Tables in SQL Server
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Real-Time Analytics
- Importance of Memory-Optimized Tables
- Understanding Memory-Optimized Tables
- What Are Memory-Optimized Tables?
- Architecture and Components
- Benefits for Real-Time Analytics
- Setting Up Memory-Optimized Tables
- Enabling In-Memory OLTP
- Creating Memory-Optimized Tables
- Defining Indexes and Constraints
- Integrating with Real-Time Data Sources
- Streaming Data Ingestion
- Handling High-Volume Transactions
- Ensuring Data Consistency
- Querying Memory-Optimized Tables
- Writing Efficient Queries
- Utilizing Natively Compiled Stored Procedures
- Optimizing Query Performance
- Monitoring and Tuning Performance
- Using Dynamic Management Views (DMVs)
- Identifying Bottlenecks
- Implementing Best Practices for Performance
- Ensuring Durability and High Availability
- Transaction Logging Mechanisms
- Checkpoint Operations
- Integration with AlwaysOn Availability Groups
- Security Considerations
- Managing Permissions
- Securing Data in Memory
- Auditing and Compliance
- Use Cases and Applications
- Financial Services
- E-Commerce Platforms
- IoT and Sensor Data Processing
- Challenges and Limitations
- Memory Consumption
- Compatibility with Legacy Systems
- Scalability Concerns
- Best Practices
- Designing for Scalability
- Implementing Robust Error Handling
- Regular Maintenance and Updates
- Conclusion
- Summary of Benefits
- Future Trends in Real-Time Analytics
1. Introduction
Overview of Real-Time Analytics
Real-time analytics refers to the process of continuously collecting, processing, and analyzing data as it becomes available. This approach enables organizations to make timely decisions based on the most current information.
Importance of Memory-Optimized Tables
Memory-optimized tables in SQL Server are designed to provide high-performance data processing by storing data entirely in memory. This design significantly reduces latency and enhances throughput, making them ideal for real-time analytics applications.
2. Understanding Memory-Optimized Tables
What Are Memory-Optimized Tables?
Memory-optimized tables are a feature of SQL Server’s In-Memory OLTP engine, introduced in SQL Server 2014. These tables are optimized for high-speed data access and are stored entirely in memory, eliminating the need for disk I/O operations.(Microsoft)
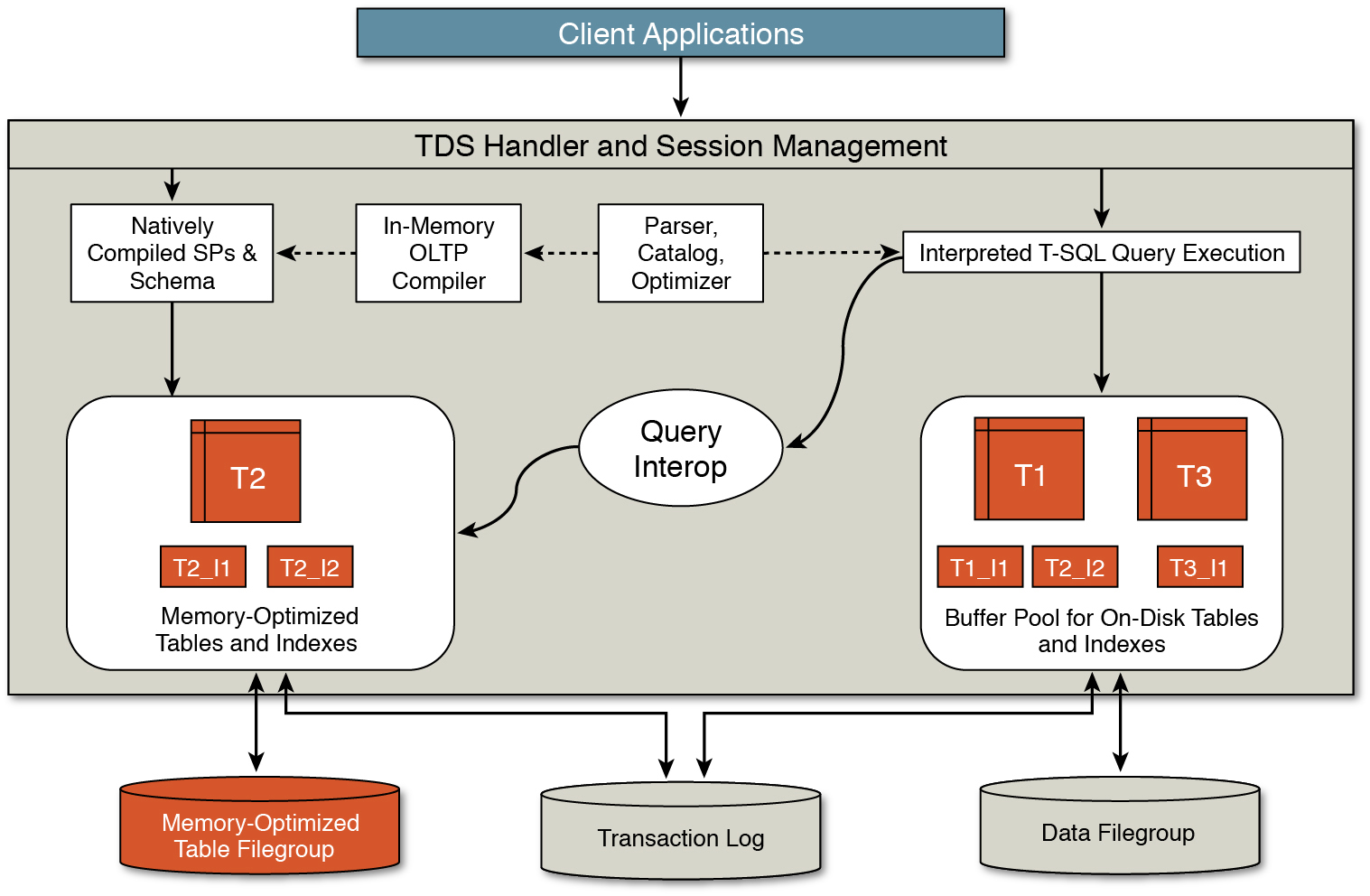
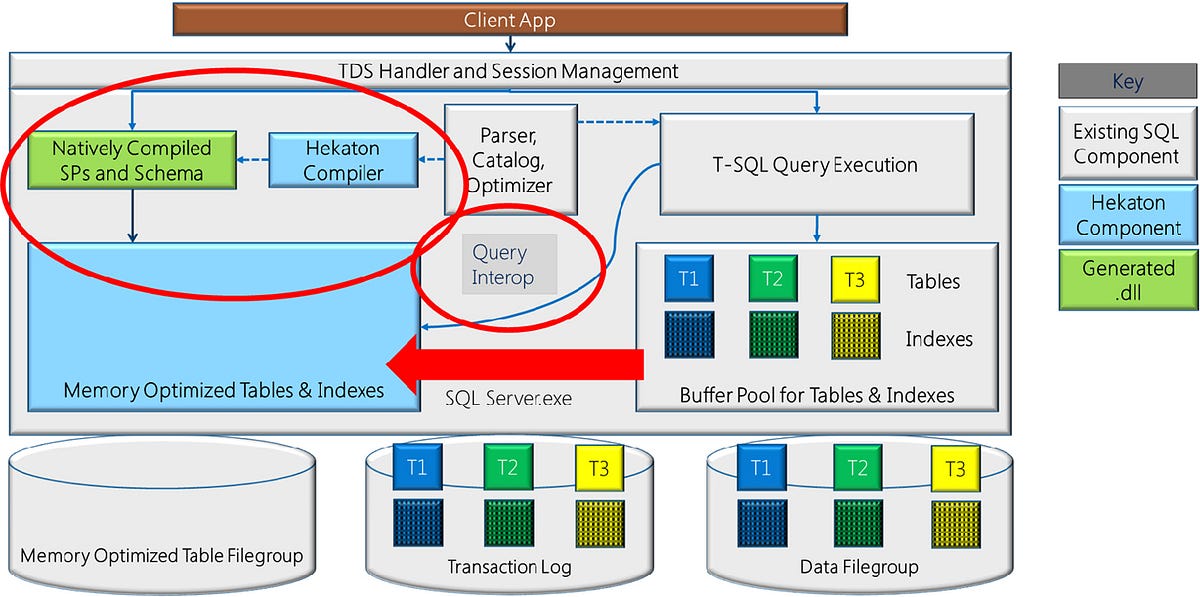
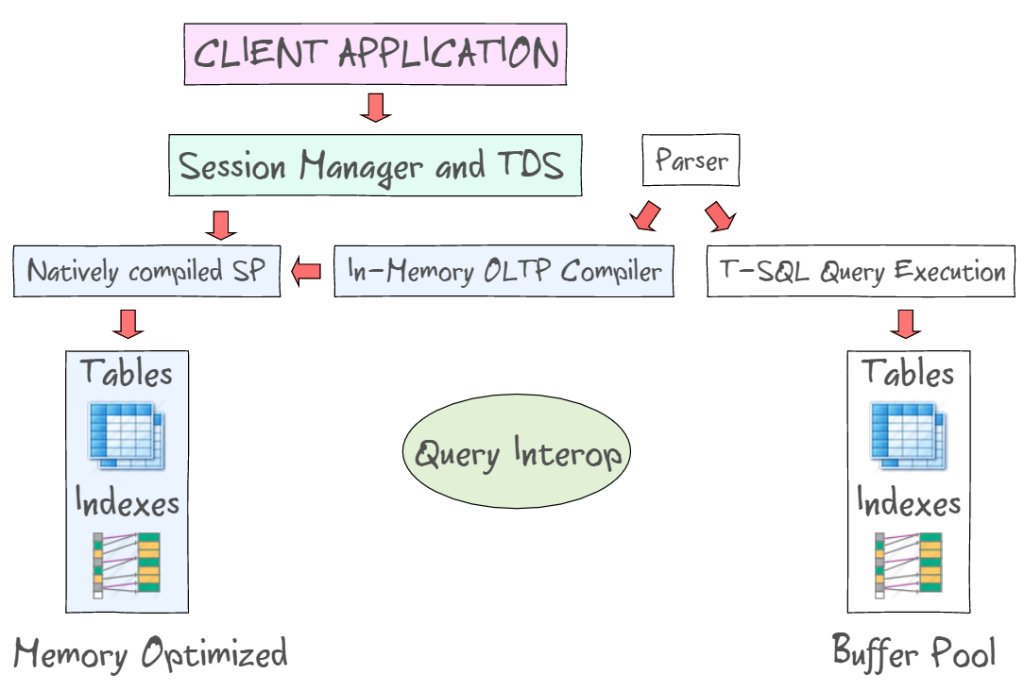
Architecture and Components
The architecture of memory-optimized tables includes:
- In-Memory OLTP Engine: Manages memory-optimized tables and natively compiled stored procedures.
- Durability Mechanisms: Ensure data persistence through transaction logging and checkpoint operations.
- Concurrency Control: Utilizes optimistic concurrency to handle multiple transactions simultaneously.(Microsoft, Microsoft)
Benefits for Real-Time Analytics
Key benefits include:(Microsoft)
- Low Latency: Fast data access and processing.
- High Throughput: Ability to handle a large volume of transactions.
- Scalability: Efficiently scales to meet growing data demands.
- Integration: Seamless integration with existing SQL Server features.(Microsoft)
3. Setting Up Memory-Optimized Tables
Enabling In-Memory OLTP
To enable In-Memory OLTP, execute the following command:
EXEC sp_configure 'clr enabled', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
This command enables CLR integration, which is required for memory-optimized tables.
Creating Memory-Optimized Tables
Use the following syntax to create a memory-optimized table:(TECHCOMMUNITY.MICROSOFT.COM)
CREATE TABLE dbo.MyMemoryOptimizedTable
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NONCLUSTERED,
Data NVARCHAR(100)
)
WITH (MEMORY_OPTIMIZED = ON, DURABILITY = SCHEMA_ONLY);
This creates a table that is stored entirely in memory.
Defining Indexes and Constraints
Memory-optimized tables support primary keys, unique constraints, and nonclustered indexes. Indexes are stored in memory and are automatically rebuilt during database recovery.(Microsoft)
4. Integrating with Real-Time Data Sources
Streaming Data Ingestion
Integrate real-time data sources using SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), Azure Stream Analytics, or custom applications that push data directly into memory-optimized tables.
Handling High-Volume Transactions
Memory-optimized tables can handle high transaction volumes due to their in-memory nature. Ensure that the system has sufficient memory resources to accommodate the expected load.
Ensuring Data Consistency
Implement appropriate transaction isolation levels and error handling mechanisms to maintain data consistency in high-concurrency environments.
5. Querying Memory-Optimized Tables
Writing Efficient Queries
Optimize queries by:
- Using natively compiled stored procedures.
- Avoiding complex joins and subqueries.
- Utilizing appropriate indexing strategies.(Microsoft)
Utilizing Natively Compiled Stored Procedures
Natively compiled stored procedures are precompiled into machine code, resulting in faster execution times. Use the following syntax to create a natively compiled stored procedure:
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.MyProcedure
WITH NATIVE_COMPILATION, SCHEMABINDING
AS
BEGIN
-- Procedure logic
END;
Optimizing Query Performance
Regularly update statistics and monitor query performance using Dynamic Management Views (DMVs) to identify and address performance bottlenecks.
6. Monitoring and Tuning Performance
Using Dynamic Management Views (DMVs)
DMVs provide insights into the performance and health of memory-optimized tables. For example

Certainly! Let’s continue our comprehensive guide on Real-Time Analytics with Memory-Optimized Tables in SQL Server, focusing on advanced topics such as performance monitoring, integration with other technologies, and best practices for deployment and maintenance.
7. Performance Monitoring and Tuning
Using Dynamic Management Views (DMVs)
SQL Server provides several DMVs to monitor the performance of memory-optimized tables:
sys.dm_db_xtp_checkpoint_stats: Provides information about the checkpoint operations for memory-optimized tables.sys.dm_db_xtp_object_stats: Displays statistics about memory-optimized tables and indexes.sys.dm_db_xtp_index_stats: Shows statistics about memory-optimized indexes.(Medium)
These DMVs can help identify performance bottlenecks and areas for optimization.
Monitoring Garbage Collection
Memory-optimized tables use garbage collection to reclaim memory occupied by deleted or updated rows. You can monitor the progress of garbage collection using the following DMV:(Microsoft)
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_db_xtp_gc_stats;
This DMV provides information about the garbage collection process, including the number of rows cleaned and the time taken.
8. Integration with Other Technologies
Combining with Columnstore Indexes
SQL Server allows the use of columnstore indexes with memory-optimized tables to enhance analytical query performance. To create a columnstore index on a memory-optimized table:(TECHCOMMUNITY.MICROSOFT.COM)
ALTER TABLE dbo.MyMemoryOptimizedTable
ADD INDEX MyColumnstoreIndex CLUSTERED COLUMNSTORE;
This combination enables real-time analytics with high-performance data retrieval.
Integration with Azure Synapse Analytics
For large-scale analytics, integrating SQL Server with Azure Synapse Analytics allows you to offload complex queries and reporting tasks. Data can be replicated from memory-optimized tables to Synapse Analytics for advanced analytics and machine learning.
9. Best Practices for Deployment and Maintenance
Designing for Scalability
- Partitioning: Implement partitioning on memory-optimized tables to distribute data across multiple filegroups, enhancing scalability and performance.
- Indexing: Use appropriate indexing strategies, such as hash indexes for equality searches and nonclustered indexes for range queries.(SQL Shack)
Implementing Robust Error Handling
Ensure that natively compiled stored procedures include error handling mechanisms to manage exceptions and maintain data integrity.
Regular Maintenance and Updates
- Statistics Updates: Regularly update statistics on memory-optimized tables to ensure optimal query performance.
- Database Backups: Perform regular backups of the database, including memory-optimized tables, to prevent data loss.
10. Conclusion
Memory-optimized tables in SQL Server provide a powerful solution for real-time analytics, offering low-latency data access and high-throughput processing. By understanding their architecture, implementing best practices, and integrating with other technologies, organizations can leverage these capabilities to gain timely insights and make data-driven decisions.
11. Further Reading and Resources
- Microsoft Documentation on In-Memory OLTP: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/in-memory-oltp/in-memory-oltp
- SQL Server Performance Tuning: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/performance/performance-tuning
- Azure Synapse Analytics Integration: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics
If you have specific questions or need further details on any of these topics, feel free to ask!
