![]()


Certainly! Let’s delve into the comprehensive process of setting up and managing subscriptions and email delivery in SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS). This guide will provide detailed, step-by-step instructions to ensure you can effectively automate report distribution.
1. Introduction to SSRS Subscriptions
What Are SSRS Subscriptions?
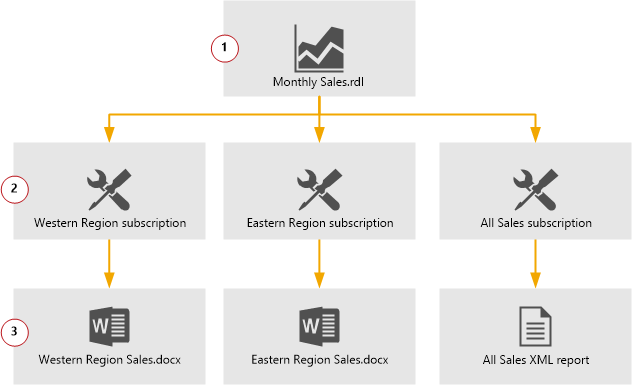
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) subscriptions allow you to automate the delivery of reports to specified recipients. There are two primary types of subscriptions:
- Standard Subscriptions: These are manually configured and scheduled to deliver reports at specified times.
- Data-Driven Subscriptions: These dynamically generate reports based on data retrieved at the time of execution, allowing for personalized deliveries.
Subscriptions can deliver reports via various methods, including email, file share, or SharePoint library. The choice of delivery method depends on the organization’s requirements and infrastructure.(BI Learning Hub)
2. Configuring Email Delivery in SSRS
2.1 Setting Up SMTP in SSRS
Before creating email subscriptions, ensure that the SSRS instance is configured to send emails:
- Open Reporting Services Configuration Manager: Launch the tool on the server where SSRS is installed.
- Navigate to E-Mail Settings: In the Configuration Manager, select the ‘E-Mail Settings’ tab.
- Configure SMTP Server:
- SMTP Server: Enter the address of your SMTP server (e.g.,
smtp.yourdomain.com). - Sender Address: Specify a default ‘From’ email address (e.g.,
reports@yourdomain.com). - SMTP Server Port: Typically, port 25 is used, but this may vary based on your SMTP server configuration.
- Authentication: If your SMTP server requires authentication, provide the necessary credentials.
- Enable SSL: If your SMTP server uses SSL, check the ‘Use SSL’ box.
- SMTP Server: Enter the address of your SMTP server (e.g.,
- Test Configuration: Click ‘Apply’ to save the settings, then use the ‘Send Test E-Mail’ feature to verify that SSRS can send emails successfully.
Once SMTP is configured, the ‘E-Mail’ option will become available when creating subscriptions.(gaurangpatel.net)
3. Creating a Standard Email Subscription
3.1 Accessing the Report Manager
- Open Report Manager: Navigate to the SSRS Report Manager URL (e.g.,
http://yourserver/reports). - Locate the Report: Browse to the report you wish to subscribe to.
- Manage Subscriptions: Click on the ellipsis (
...) next to the report name and select ‘Manage’. - Navigate to Subscriptions: In the left-hand menu, click on ‘Subscriptions’.(MSSQL Tips)
3.2 Creating the Subscription
- New Subscription: Click on ‘New Subscription’.(MSSQL Tips)
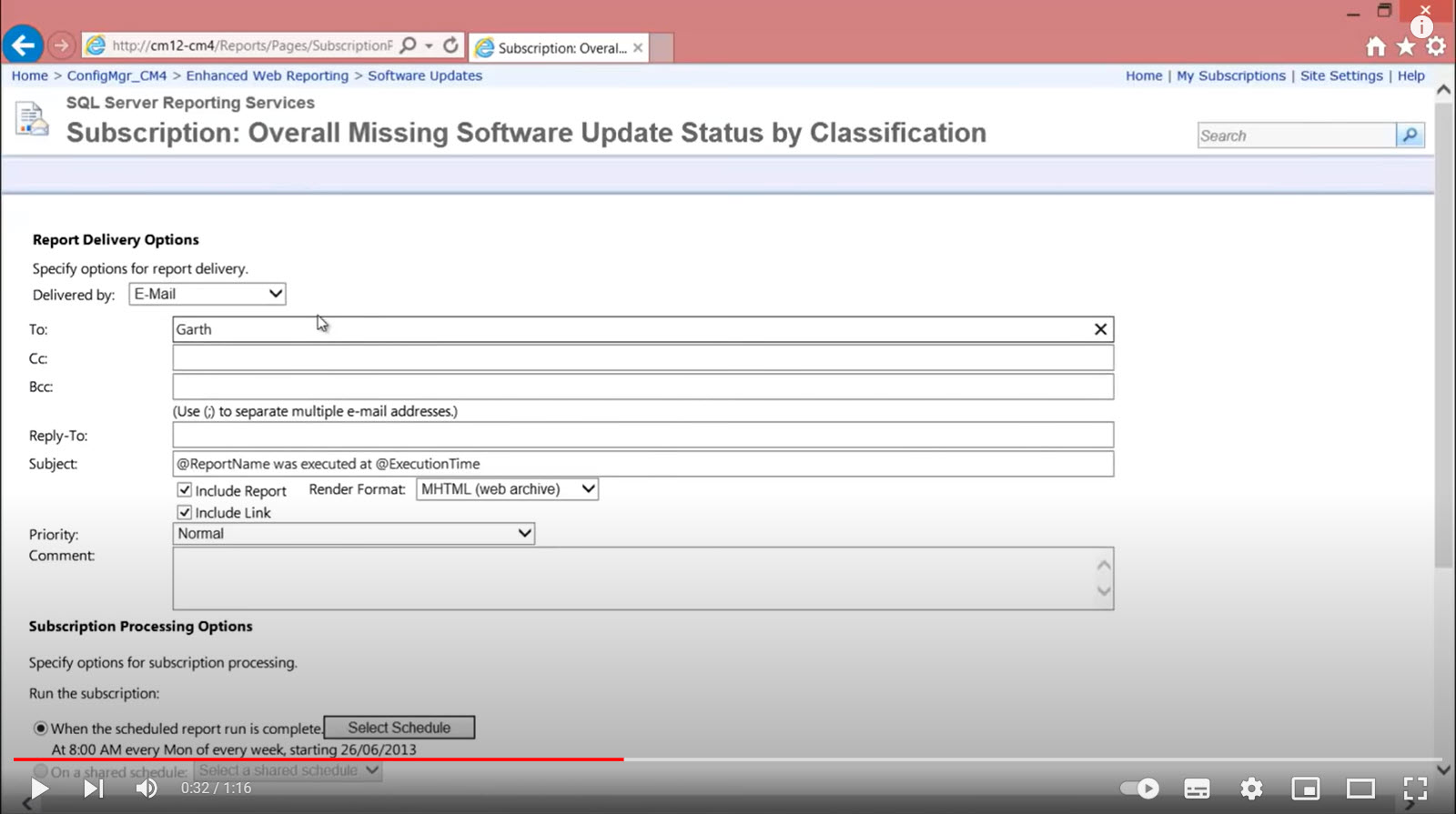
- Choose Delivery Method: Select ‘E-Mail’ as the delivery method.
- Configure Subscription Settings:
- Description: Provide a name for the subscription (e.g., ‘Daily Sales Report’).
- Delivery Settings:
- To: Enter recipient email addresses (e.g.,
sales@yourdomain.com). - CC/BCC: Optional fields for additional recipients.
- Subject: Specify the subject line (e.g., ‘Daily Sales Report – [ExecutionTime]’).
- Include Report: Choose whether to include the report as an attachment.
- Render Format: Select the desired format (e.g., PDF, Excel, Word).
- Include Link: Decide whether to include a link to the report in the body of the email.
- Priority: Set the email priority (e.g., Normal, High).
- To: Enter recipient email addresses (e.g.,
- Schedule Subscription:
- Schedule Type: Choose the frequency (e.g., Daily, Weekly, Monthly).
- Start Time: Specify when the subscription should begin.
- End Time: Optional field to set when the subscription should end.
- Parameter Settings (if applicable):
- If the report has parameters, specify the values to be used for the subscription.
- Save Subscription: Click ‘OK’ to save the subscription.
The report will now be delivered via email according to the specified schedule.(gaurangpatel.net)
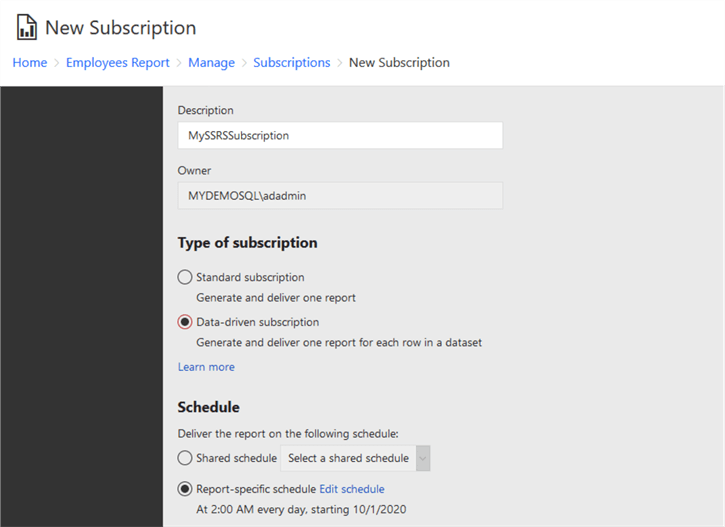
4. Creating a Data-Driven Subscription
4.1 Understanding Data-Driven Subscriptions
Data-driven subscriptions allow for more dynamic and personalized report deliveries. Instead of manually specifying recipients, SSRS queries a data source to determine who should receive the report and in what format.
4.2 Configuring the Data Source
- Access Report Manager: Navigate to the SSRS Report Manager URL.(BI Learning Hub)
- Manage Report: Locate the report, click on the ellipsis (
...), and select ‘Manage’.(MSSQL Tips) - Subscriptions: Click on ‘Subscriptions’ in the left-hand menu.
- New Data-Driven Subscription: Click on ‘New Data-Driven Subscription’.(BI Learning Hub)
- Data Source:
- Use Shared Data Source: Select an existing shared data source.
- Specify Data Source: Provide a connection string and credentials for a new data source.(BI Learning Hub)
- Query: Enter a SQL query that returns a result set with the necessary fields (e.g., email addresses, report formats).
Certainly! Let’s continue our detailed exploration of subscriptions and email delivery in SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), focusing on advanced features, best practices, and troubleshooting.
5. Advanced Features in Data-Driven Subscriptions
5.1 Conditional Subscriptions
In scenarios where reports should only be delivered under certain conditions, you can implement conditional logic within your data-driven subscription’s query. For instance, you might want to send a report only if certain business criteria are met, such as the completion of a specific process or the occurrence of a particular event.
Example:
DECLARE @CurrentDate DATE = GETDATE();
DECLARE @ProcessCompletionDate DATE = (SELECT ProcessCompletionDate FROM ProcessStatus WHERE ProcessID = 123);
IF @CurrentDate > @ProcessCompletionDate
BEGIN
SELECT EmailAddress, ReportFormat FROM ReportRecipients WHERE IsActive = 1;
END
This query checks if the current date is greater than the process completion date and, if so, retrieves the email addresses and preferred report formats of active recipients.
5.2 Handling Multi-Value Parameters
Passing multi-value parameters in data-driven subscriptions can be challenging, as SSRS expects a single value for each parameter. To work around this limitation, you can pass a concatenated string of values and then split them within the report.
Example:
SELECT EmailAddress, ReportFormat, 'Value1,Value2,Value3' AS MultiValueParam FROM ReportRecipients;
In the report, you can then split this string into individual values using the Split function.
Note: Ensure that the concatenated string does not exceed the maximum length allowed for SSRS parameters.
5.3 Dynamic File Naming
When delivering reports to a file share, you may want to generate dynamic file names based on report parameters. This ensures that each report is uniquely identifiable.
Example:
SELECT EmailAddress, ReportFormat, CONCAT('Report_', UserID, '_', FORMAT(GETDATE(), 'yyyyMMdd_HHmmss'), '.', ReportFormat) AS FileName FROM ReportRecipients;
This query creates a unique file name by combining the user ID, current date, and time, along with the desired report format.
6. Troubleshooting Common Issues
6.1 Empty Reports
One common issue with data-driven subscriptions is the delivery of empty reports. This can occur if the query returns no rows or if the report parameters are not correctly mapped.(MSSQL Tips, Ray Barley’s SSRS Notes)
Solution:
- Ensure that the query returns the expected rows.(Ray Barley’s SSRS Notes)
- Verify that the report parameters are correctly mapped to the query results.
- Check the report’s data source and credentials to ensure they are valid and have the necessary permissions.
6.2 Subscription Not Triggering
If a subscription is not triggering as expected, it could be due to several reasons:
- Query Execution Time: If the driving query takes longer than 30 seconds to execute, SSRS may not trigger the subscription. This is a known limitation in certain versions of SSRS. (Microsoft Support)
- Data Source Credentials: Ensure that the data source credentials are correctly configured and have the necessary permissions.
- Subscription Schedule: Verify that the subscription is scheduled correctly and that the report server is running.
6.3 User Profile Dependencies
Data-driven subscriptions cannot be created if the report or shared dataset has user profile dependencies, such as the use of User!UserID. This is because data-driven subscriptions run in unattended mode and cannot evaluate user-specific expressions. (eugenechiang.com, prologika.com)
Solution:
- Avoid using
User!UserIDin the report or dataset.(prologika.com) - If user-specific data is required, consider passing the user ID as a parameter from the data-driven subscription query.
7. Best Practices
7.1 Secure Delivery
When delivering reports via email, ensure that the email server is configured securely to prevent unauthorized access. Use secure connections (e.g., SSL/TLS) and authenticate the sending server.
7.2 Monitor Subscription Status
Regularly monitor the status of subscriptions to ensure they are running as expected. SSRS provides a subscription history feature that allows you to view the status and any errors associated with each subscription.
7.3 Optimize Query Performance
Ensure that the queries used in data-driven subscriptions are optimized for performance. Long-running queries can delay report delivery and impact server performance.
7.4 Use Stored Credentials
For scheduled reports and subscriptions, use stored credentials to ensure that the report server can access the necessary data sources without requiring user interaction.
Subscriptions and email delivery in SSRS provide powerful tools for automating the distribution of reports. By understanding the different types of subscriptions, configuring them correctly, and following best practices, you can ensure efficient and secure report delivery. Always consider the specific requirements of your organization and the capabilities of your SSRS environment when implementing subscriptions.
If you have further questions or need assistance with specific configurations, feel free to ask!
